Hi again!
We thought it might be beneficial to create a post entailing things we have learned over the course of this semester about fluency that have been helpful to us!
Fluency is defined as speech production that is:
- Continuous
- Smooth
- Made at a culturally appropriate rate
- Made with an acceptable degree of effort
There are some “Red Flags” to consider when assessing a person who may have a fluency disorder. This “red flags” are indicators of a higher probability of stuttering:
- Family history of stuttering – Specifically mother
- Gender – Males being at a higher risk
- Stuttering for more than 6 months
- Speech and language deficits
- Age of onset – Children who beginning stutter before 3.5 years are more likely to spontaneously recover
It is important consider that when a child is around the age of three their vocabulary and language are exploding. It is developmentally appropriate for a child to experience dysfluencies at this age. It is generally characterized by repetitions of whole words and phrases, instead of a single phoneme or sound. If the child is exhibiting developmentally appropriate dysfluencies, they should not show any tension or frustration. A child that exhibits these affective behaviors likely has awareness of their dysfluencies which is a red flag for stuttering.
Also of mention, are linguistic dysfluencies. These are defined as hesitations used to maintain a conversational turn, fillers used when word finding is impacting, and typical interjections (e.g. “uh,” “um”). These are experienced by all of us each day and are not considered disordered.
Here is a visual from https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/toddler/Pages/Stuttering-in-Toddlers-Preschoolers.aspx that may be helpful is ruling out stuttering:
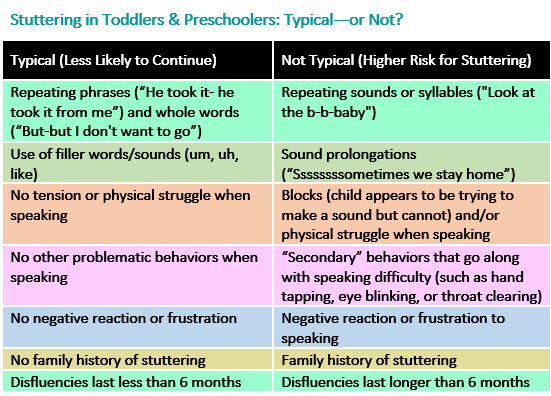
Types of Stuttering:
Blocks: This happens when a person has a hard time getting a word out. The person my pause for a long time or not be able to make a sounds. For example: I want a …….. million dollars.
Prolongations: A person may stretch a sound out of a long time. For example: mmmmmmoney.
Repetitions: A person may repeat parts of words. For example, mo-mo-money
Types of Therapy:
Fluency shaping: In this technique the goal is:
1.Controlled fluency
2.Spontaneous fluency
3.Normal fluency
Stuttering Modification: In this technique the goal is aiming towards spontaneous fluency, controlled fluency, acceptable stuttering. The idea is more so to modify the way a person stutters, rather than normal fluency.
Helpful Links:
https://www.asha.org/public/speech/disorders/stuttering.htm
Let us know if you have any more helpful links or information regarding stuttering!
Best,
A, H, + M